What are ERP and MRP software
In a manufacturing company where efficient resource management is critical, enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing resource planning (MRP) systems play a crucial role.
Both systems focus on resource planning and management, but there are significant differences between ERP and MRP.
Read this article to find out what the main features and benefits of each system are and how they can interact with each other to help you optimize your business.
MRP meaning
First of all, what does MRP mean? In the manufacturing world, the acronym refers to material requirements planning software systems, English: Material Requirements Planning.
An MRP system is designed to optimize production and inventory management. Its main function is to ensure that the materials needed for production are available at the right time and in the required quantities to keep production efficient and reduce downtime.
These software solutions are particularly useful in the manufacturing industry because their main purpose is to determine what materials are needed, in what quantities and when, so as to ensure that production runs smoothly and that inventories are kept at optimal levels. This avoids productivity losses due to downtime.
The MRP system focuses on the scheduling of material procurement activities, from order planning to raw material purchasing and inventory management.
The successful implementation of a Material Requirements Planning depends on the accuracy of input data, such as sales forecasts, production and purchasing lead times, and current inventory levels.
The basic objectives of an MRP system include:
-
Efficient inventory management: One of the main objectives of MRP is to ensure that material inventories are optimally managed. This means that materials needed for production must be available at the right time and in the right quantity, avoiding both shortages and overstocking. The MRP helps determine supply needs and plan purchase or production orders to maintain an optimal inventory balance.
-
Delivery time optimization: MRP aims to ensure that finished goods are delivered to customers on time. Using information on inventory, production capacities, and customer requirements, the MRP system helps plan and coordinate production activities so that agreed delivery times are met.
-
Production planning: Another key objective of MRP is to plan production efficiently. This involves determining production times, allocating resources, and scheduling activities to meet customer demand. The MRP takes into account factors such as processing times, machine capacities, and labor availability to create an optimized production plan.
-
Waste and cost reduction: An important goal of MRP is to reduce material waste and minimize production costs. Through efficient inventory management and careful planning, MRP helps to avoid overproduction, accumulation of obsolete stock, and wastage of resources. This helps to reduce production costs and improve the company's overall profitability.
- Improved visibility and traceability: The MRP provides a clear and comprehensive view of production resource management information. It enables tracking of materials, inventories, production ordinances, and schedules, providing real-time visibility into business operations. This enables informed decision-making and rapid response to changes in customer needs or market conditions.
Appearing in the 1960s, MRP systems have evolved over time to meet increasing product complexities and new market challenges.
There has been a shift from systems focused primarily on material management for production to systems that include planning and management of all business resources involved in the production process, including critical aspects such as machine capacity management, workforce and financial planning activities, and quality control.
From planning, to forecasting, to cost control, every aspect of production must be aligned to create the desired results without waste.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are designed for this need.
ERP meaning
Developed from existing functionality in MRP II systems,ERP (short for Enterprise Resource Planning) is a broader system that integrates and manages all aspects of the enterprise, including production, human resource planning, finance management, logistics, sales and more.
ERP goes beyond materials management and involves other business functions to create a complete picture of business activity.
I ERP management systems provide a unified, real-time view of business operations, enabling greater control, greater efficiency, and better decision making.
Here are some of the main benefits of an ERP system for manufacturing companies:
-
Business process integration: An ERP system integrates all business processes, from inventory management and sales to production and accounting. This integration provides greater visibility and control over all phases of the operation, enabling more accurate planning, reduced errors, and overall improved operational efficiency.
-
Production planning and management: An ERP system provides advanced functionality for production planning and management. It allows you to define processing times, monitor machine capacities, manage human resources, and plan production according to customer requirements. This enables optimal use of resources, minimizing waste and ensuring faster lead times.
-
Inventory management: ERP enables efficient inventory management, optimizing inventory levels and reducing the risk of obsolete or excessive inventory. With features such as purchase order management, inventory control, and material requisition planning, companies can maintain a balance between inventory availability and market demand.
-
Quality monitoring and control: A manufacturing ERP system can include modules for quality monitoring and control. These modules enable quality standards to be set, test results to be recorded and tracked, and nonconformities to be managed. This helps companies maintain high quality standards, minimizing defects and improving customer satisfaction.
-
Reporting and analysis: An ERP system provides powerful reporting and analysis tools to monitor business performance. Through customizable dashboards, predefined reports, and real-time data analysis, companies can gain a detailed view of their operations, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to optimize overall performance.
-
Improved collaboration: An ERP system promotes collaboration among business departments. Information is shared in real time among different functions, enabling more efficient communication, better coordination of activities, and reduced duplication and errors.
- Adaptability and scalability: An ERP system can be adapted to the specific needs of a manufacturing company and can grow with the company. It can support different product lines, complex manufacturing processes and industry-specific requirements, enabling companies to adapt to market changes and grow sustainably.
What is the relationship between an ERP system and an MRP system?
An enterprise resource planning (ERP) system and a material requirements planning (MRP) system are closely related but differ in their purpose and scope of functionality.
The MRP is a subset of the ERP system that focuses on managing the materials needed for production, while the ERP embraces a broader view and includes functionality to manage all enterprise resources in an integrated manner.
ERPs are modular, so the company can choose the modules most useful for its business; starting with an "all-in-one" ERP such as our Target Cross, modules and features can be integrated (even at a later date) into a single database .
In addition, while MRPs are used largely by production and materials procurement personnel, ERP on the other hand can be used by a wider range of departments, including those predisposed to financial planning, human resource management, marketing or customer relations.
ERP and MRP: which one is best for your company?
When it comes to choosing an ERP system, it is important to considerMRP integration as a key factor.
The ability to handle both finance and materials management within a single platform offers numerous advantages.
First, ERP-MRP integration enables improved accuracy of production forecasting, as financial data and material information can be correlated and analyzed together. This facilitates resource planning and alignment, reducing waste and improving overall efficiency.
In addition, an ERP system that also manages MRP provides better visibility and control of business operations. Material flow, lead times, inventory management, and production planning can be more accurately monitored and managed. This level of control enables rapid response to changes in the market and greater ability to adapt to customer needs.
Finally, the integration of MRP within an ERP system promotes collaboration and communication between business departments. Production, purchasing, sales, and finance teams can share information in real time and work together to achieve common business goals. This synergy between departments leads to greater operational efficiency and improved customer satisfaction.
Target Cross®: the ERP solution that manages the MRP
Target Cross® is a modular, extended ERP solution that enables management of the master production plan (MPS) and materials planning and procurement (MRP).
A single management software solution that also integrates MRP and MPS into the ERP system to make the various production steps more streamlined, faster and immediate, both long and short term.
In particular, with Target Cross it is possible to optimize the steps of:
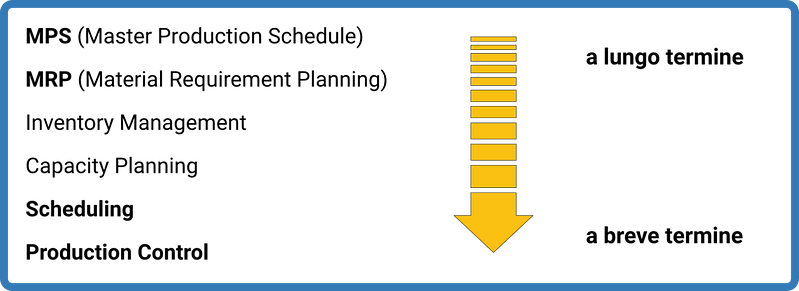
DueEsseTi is a Target Cross® partner for Lombardy and Piedmont. Contact us for all your ERP and MRP needs.
Learn about our ERP solutions for the manufacturing sector



